RPA in Automotive Manufacturing:
From Manual Tasks to Measurable ROI
“By 2025, 50% of all RPA deployments will occur in manufacturing, logistics, and energy sectors.”- Gartner, Future of RPA in Industrial Sectors
Let’s Talk About Robotic Process Automation, the Robots Behind the Robots
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) isn’t the kind of robot that bolts fenders or welds chassis. It’s the invisible kind – the digital assistant that quietly handles everything from test data logging to compliance paperwork. And in today’s automotive factories, where vehicles are increasingly defined by their electronics, RPA is becoming the secret weapon for staying accurate, fast, and audit-ready.
For high-spec modules like digital rearview mirrors, ADAS sensors, and infotainment units – all packed with firmware, optics, and delicate components – RPA is the only way to keep up with quality expectations while ditching manual busywork that slows everyone down.
You can’t scale precision manually. You either automate or you accept defects.” – Dr. Hanno Eiden, Advisor, Automotive Electronics & Vision Systems
Why Automotive Manufacturing Is Still Stuck in Manual Mode
Let’s be honest: the assembly line has come a long way, but the backend? Still a mess of checklists, spreadsheets, and clipboard heroes. Here’s what’s still going wrong:
- Camera Module Misalignment: One shaky hand or a misused jig, and suddenly your digital mirror is pointing at the sky.
- Optical Clarity Checks: Humans inspecting screens and lenses with their eyeballs. Spoiler alert: they miss about 15% of defects.
- Connector Assembly & Wiring: Tiny plugs, big consequences. One loose connector = field failures and warranty claims.
- Firmware Uploads: One wrong software version flashed, and you’ve just made 300 defective units.
- Manual Logging: Still writing down serial numbers? Mislabelling and data gaps aren’t just annoying – they’re a liability.
These tasks don’t just introduce risk; they guarantee rework and delays. And when every second and SKU counts, RPA turns “good enough” into “done right, first time.”
“Only 29% of auto manufacturers currently automate their production documentation.”- Capgemini Research Institute, Smart Factories Report
Where RPA Does the Heavy Lifting (Quietly, Relentlessly, 24/7)
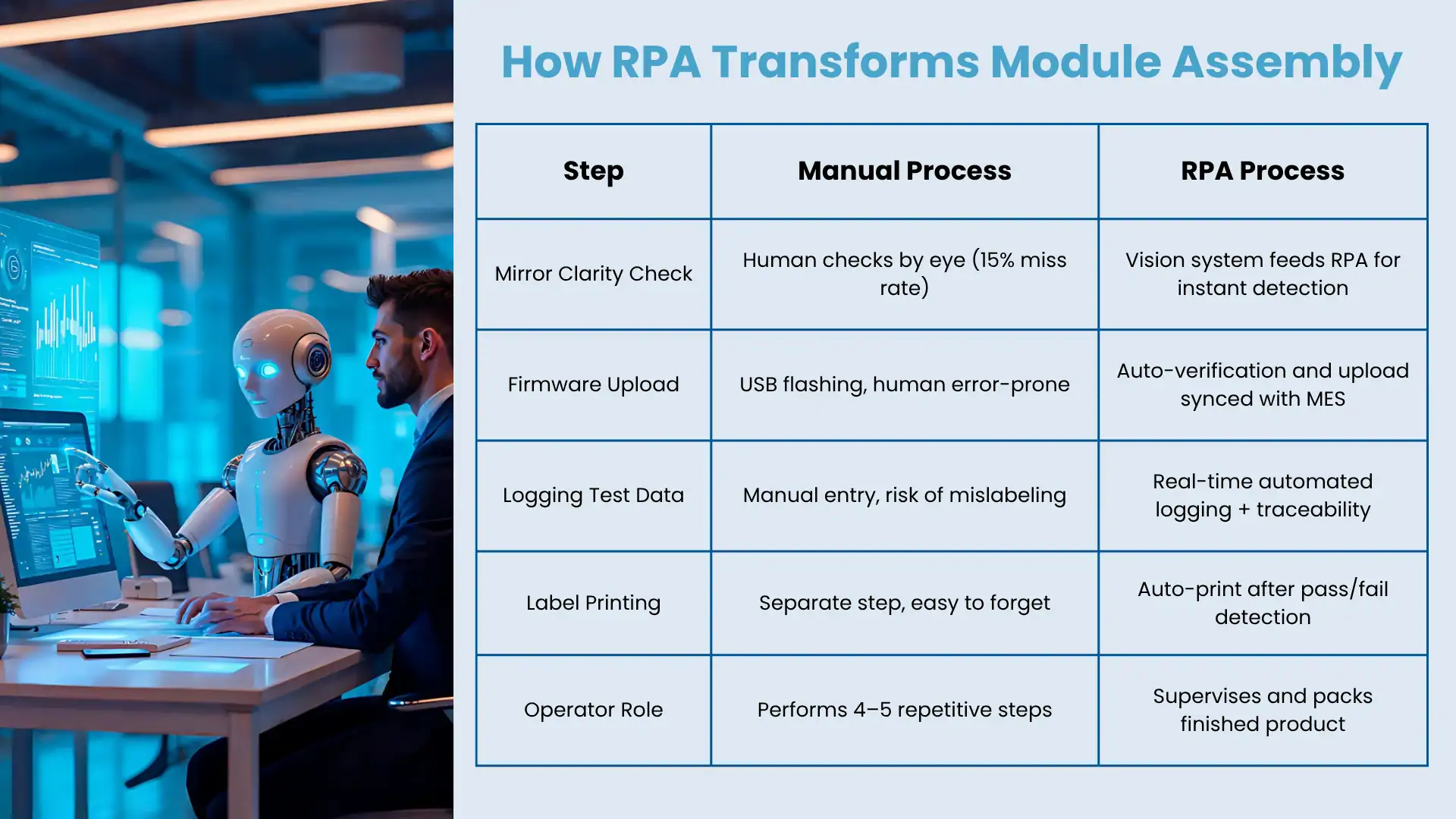
Take digital mirrors. Every unit needs its camera feed checked for clarity, its firmware version verified, its test results logged, and its compliance label printed. In a manual world, this means at least three people, four systems, and a whole lot of reworks when something gets skipped.
That’s not automation for automation’s sake. That’s a digital co-worker quietly catching the small stuff before it becomes a big, expensive problem.
Here’s how RPA flips the script on high-precision electronic module assembly:
Automated Quality Gatekeeper
- Vision systems feed data to RPA bots that compare clarity, colour accuracy, and distortion against spec – instantly.
- Instead of waiting for a failed audit, the bot flags blur, misfocus, or bad displays on the spot.
Sensor & Software Checkpoints
Ambient light sensor? Gyroscope? Firmware version? RPA runs calibration and verification routines in sync with the line – no skipped steps, no surprises.
Predictive Monitoring, Not Just Reaction
- Tool torque trending too high? Assembly oven off-temp? RPA pulls the data in real time and warns you before things go sideways.
- That includes watching environmental conditions that can silently wreck adhesives or sensors.
Traceability & Compliance on Autopilot
- Each unit’s test data, component batch, and software version are logged without anyone touching a keyboard.
- If there’s a recall (or worse, a lawsuit), RPA already knows exactly which units were affected.
These aren’t theoretical. They’re the use cases delivering ROI today in plants dealing with electronics-heavy components.

“Think of RPA as a digital lean engineer. It doesn’t forget, it doesn’t skip steps, and it works 24/7.” – Forrester Research
The Real Payoff: What RPA Actually Delivers
The gains aren’t theoretical. Manufacturers using RPA in their production environments have reported:
- 60% fewer defects: Bots don’t skip steps or mislog test data.
- 95% faster reporting: What took 3 hours now takes 10 minutes.
- $900K+ saved/year: One supplier automated invoice and quality report workflows.
- Audit prep time cut in half: Because the documentation was already done, in real time, every time.
Oh, and employees? They’re not replaced – they’re relieved. Now they can focus on engineering and problem-solving instead of chasing serial numbers across four systems.
“Most of the industry still uses Excel sheets and barcode stickers for traceability. That’s fine—until you face a recall.” – Plant Manager, Tier-1 Auto Supplier (anonymous, via Deloitte Survey)
A Quick Hypothetical That’s Anything But Far-Fetched
Before RPA:
Operators visually check mirror clarity. Manually log test results. Flash firmware via USB. Stick a label on. Hope they didn’t forget step 3.
After RPA:
The bot captures image sharpness from the camera feed. Logs it. Checks firmware version. Prints a traceable label. Sends the unit down the line. Operator? Just packs it.
Result?
+20% throughput. Fewer defects. Zero compliance gaps. No one got buried in paperwork.
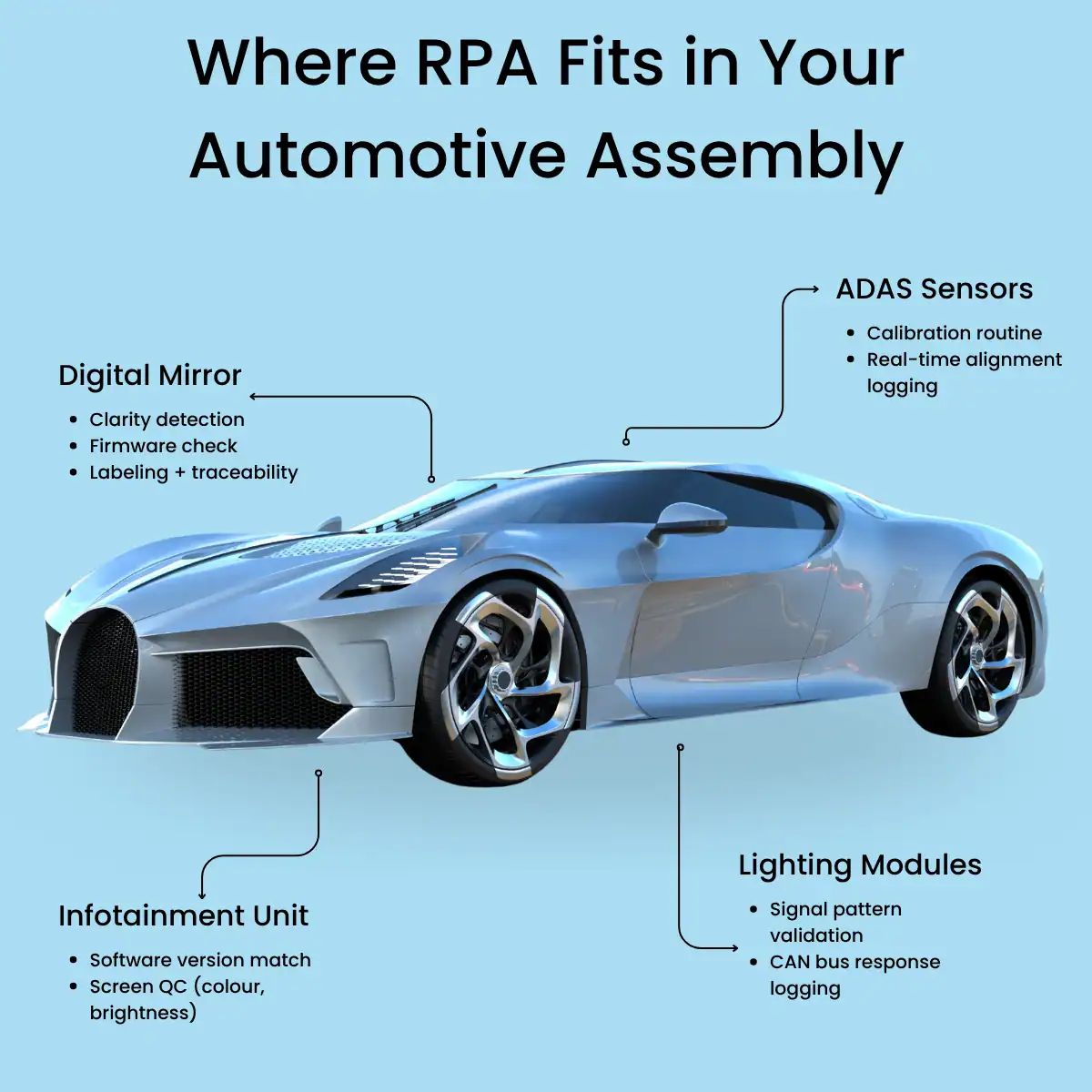
It’s Not Just Digital Mirrors
This same model applies to:
- ADAS sensor clusters (alignment and calibration)
- Infotainment modules (firmware verification, screen QA)
- Lighting systems (pattern and signal validation)
Any module with electronics, software, and traceability requirements is a playground for RPA.
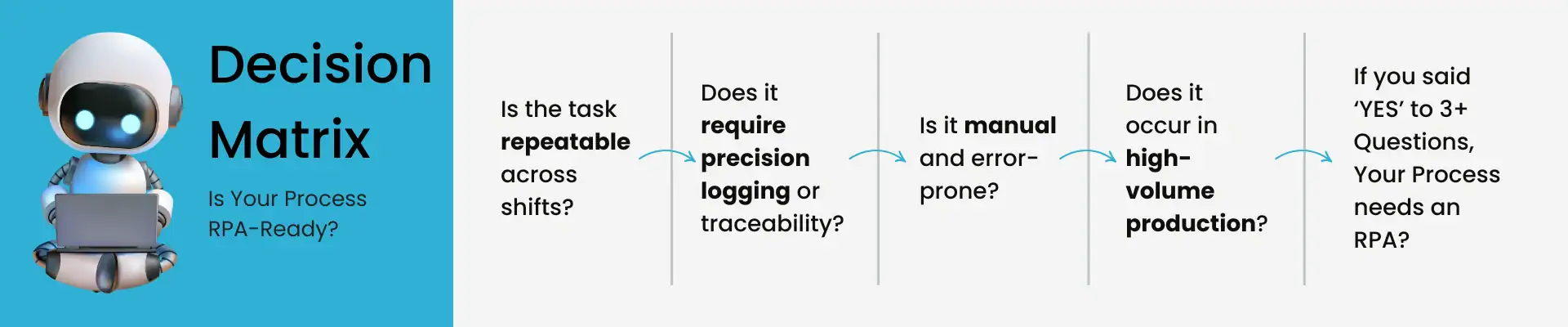
“The best RPA candidates are repetitive, rules-based, and frequent tasks — especially those tied to compliance.” – UiPath, RPA in Manufacturing Guide
Next Moves: What You Should Be Doing Now (infographic)
- Audit Your Processes
Start with one line. Where are the repeatable, manual, error-prone steps? There’s your shortlist. - Pilot a Use Case with Teeth
Pick one pain point. Logging test results? Compliance reports? Get a bot running. Watch the impact. - Track the ROI
Time saved. Errors reduced. Money not wasted. You’ll have real data – and a blueprint to scale.
RPA Isn’t Flashy. It’s Just Smart.
You don’t need an AI overlord or a robot army. You need reliable, repeatable, boring tasks done perfectly. Every time. That’s what RPA delivers – and why digital mirror lines and other module factories are quietly upgrading their operating system without rewriting their whole playbook.
Ready to move from manual frustration to measurable performance?
Let the bots take it from here.
Explore more related content
Strategic Global Sourcing: How Companies Move from Cost Saving to Competitive Advantage
Strategic Global Sourcing: How Companies Move from Cost Saving to Competitive AdvantageSupply chain disruptions now...
Critical Minerals, Critical Thinking: Building Resilient Electronics Supply Chains
Critical Minerals, Critical Thinking: Building Resilient Electronics Supply ChainsThe global economy is expected to...
Cybersecurity for Smart Factories: A 2025 Playbook for OT Resilience
Cybersecurity for Smart Factories: A 2025 Playbook for OT ResilienceWhy "smart" now means "secure" or not at all Smart...